POSTED
September 6, 2024
Agrivoltaics: Is Dual Use the Future of Solar Farming?
Solar energy is here to stay. The United States alone is projected to install around 45 gigawatts (GW) of utility-scale solar farms in 2024. This boom in solar projects is due in large part to technological advancements, supportive government policies, and the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.

While solar energy has a net positive impact on the environment, there are some downsides. Namely, utility-scale solar farms require large amounts of land, often hundreds of acres, to generate significant amounts of electricity. This extensive land use can lead to habitat disruption and loss of agricultural or natural land, negatively impacting local ecosystems and decreasing biodiversity.
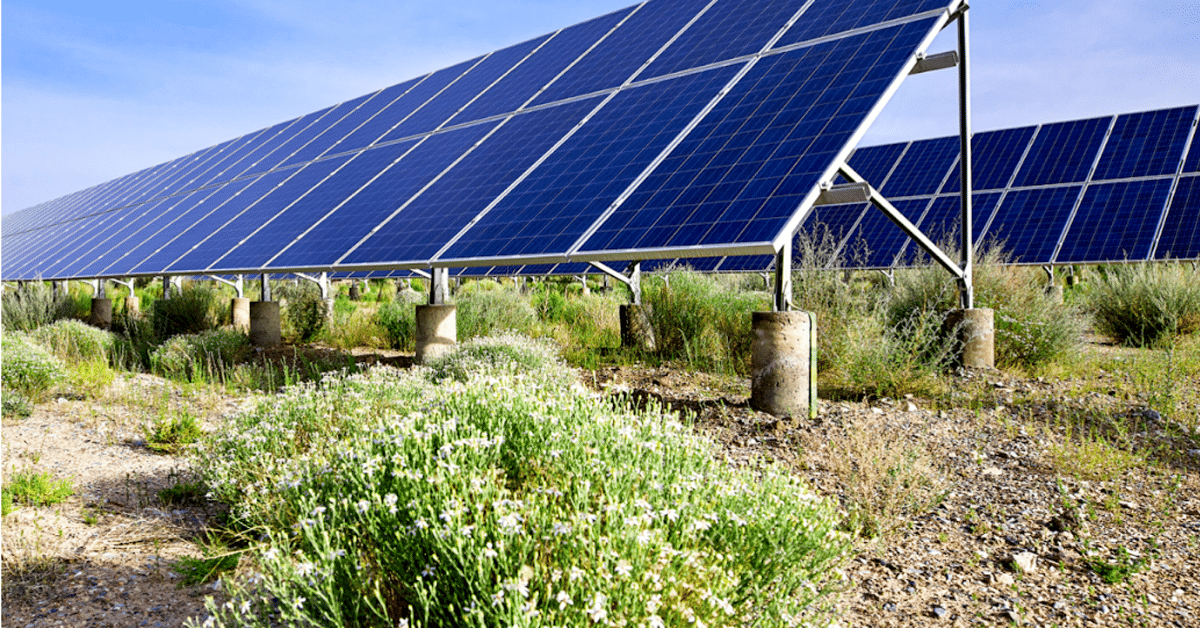
There is, however, a way to mitigate this downside. Also known as dual-use solar farming, agrivoltaics is an innovative approach that integrates solar power generation with agriculture. It aims to maximize the productivity and efficiency of land use by allowing for the simultaneous production of agricultural products like food, wool, or hay and renewable energy.
What is Agrivoltacis?
Agrivoltaics, also known as dual-use solar, is the practice of using the same land for both agriculture and solar energy production. This approach involves installing solar panels on farmland to allow crops to grow beneath them or livestock to graze, maximizing the land’s utility. Agrivoltaics is a growing field of interest addressing the dual challenges of food security and the need for renewable energy. This makes it a compelling solution for sustainable development.
The concept dates back to the early 1980s. German physicist Adolf Goetzberger first proposed the idea of combining agriculture and solar energy production to address land scarcity, food security, and increasing energy demand. While the idea has been around for over 40 years, the first practical implementations of agrivoltaic systems began appearing in the 2000s. These early projects were small-scale and primarily experimental.
Agirvoltaics really gained traction as a viable commercial solution in the 2010s when countries like Japan, Germany, and the United States started implementing large-scale agrivoltaic projects. For example, the Fukushima Agrivoltaic Project in Japan grows seven types of grapes under solar panels. This allows for continuous agricultural use while generating about 3.7 million kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity annually.
In recent years, supportive policies and incentives have further accelerated the adoption of agrivoltaic systems. Technological advancements have also significantly improved the efficiency and practicality of agrivoltaic systems.
Environmental Benefits
Agrivoltaic systems allow for the simultaneous use of land for agriculture and solar energy production. This dual-use approach maximizes the productivity of the land, particularly in areas where land is scarce and expensive. The shade provided by solar panels also reduces evaporation, helping to retain soil moisture. This can decrease the need for irrigation and conserve water resources. In fact, studies have shown that soil moisture remained approximately 15% higher in agrivoltaic systems compared to traditional farming practices.
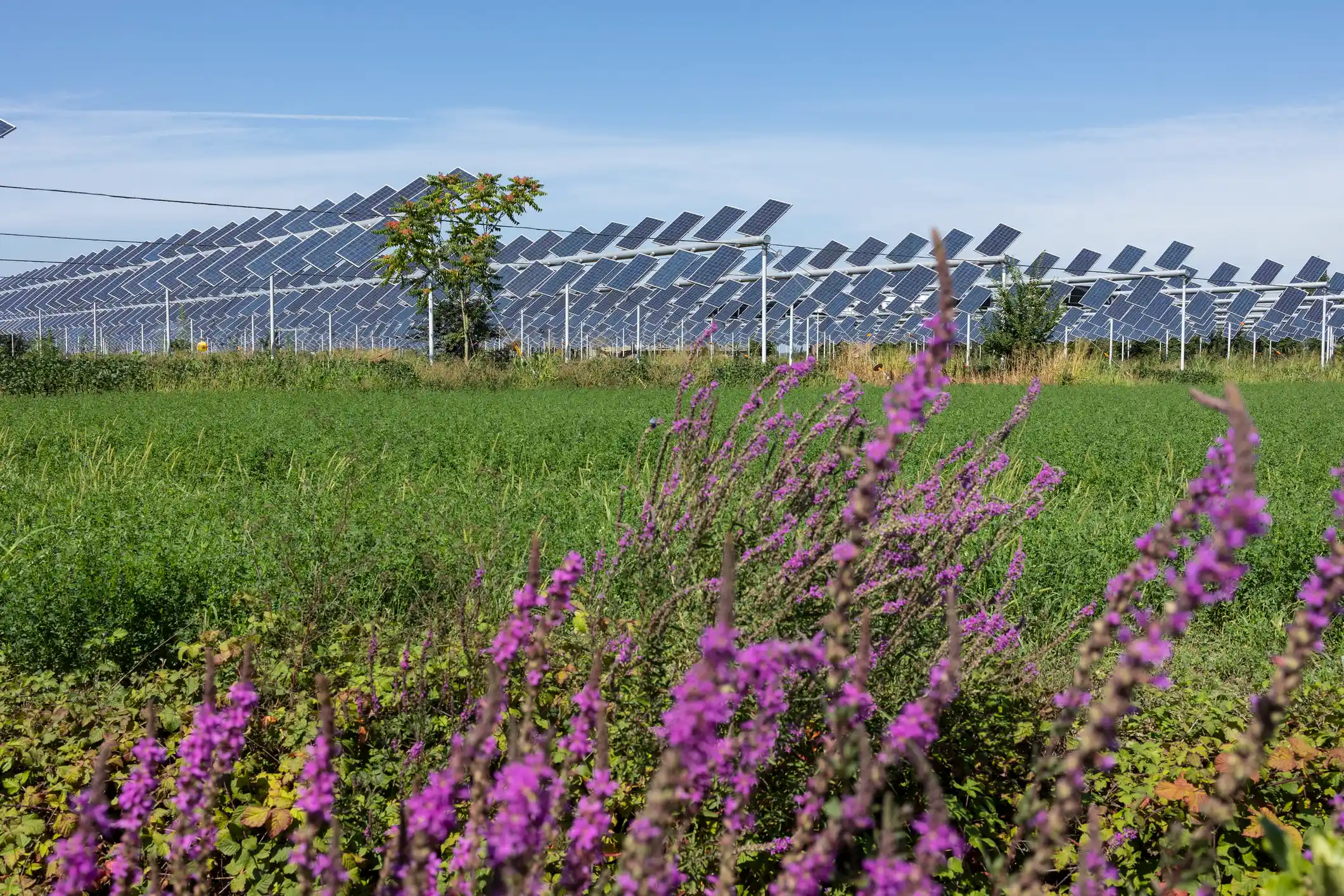

By integrating native vegetation and pollinator-friendly plants under and around solar panels, agrivoltaics can help promote biodiversity. This approach creates habits for various species and enhances the area’s ecological health.
Economic Benefits of Agrivoltaics
Agrivoltaics can help farmers diversify their revenue streams. By leasing parts of their land for utility-scale solar projects, they can have a steady stream of rental income. This can help provide financial stability, especially during times when crop yields are low from adverse weather or market fluctuations.
While it might seem counterintuitive, agrivoltaics can increase crop yields and quality. For instance, certain crops benefit from partial shade. The shading provided by solar panels can help protect these crops from extreme heat and reduce water stress.
The installation and maintenance of agrivoltaic systems generate jobs, contributing to local economic growth. These projects also often require collaboration with agronomists, agricultural firms, and other stakeholders, further driving regional development.
Agrivoltaics in Action
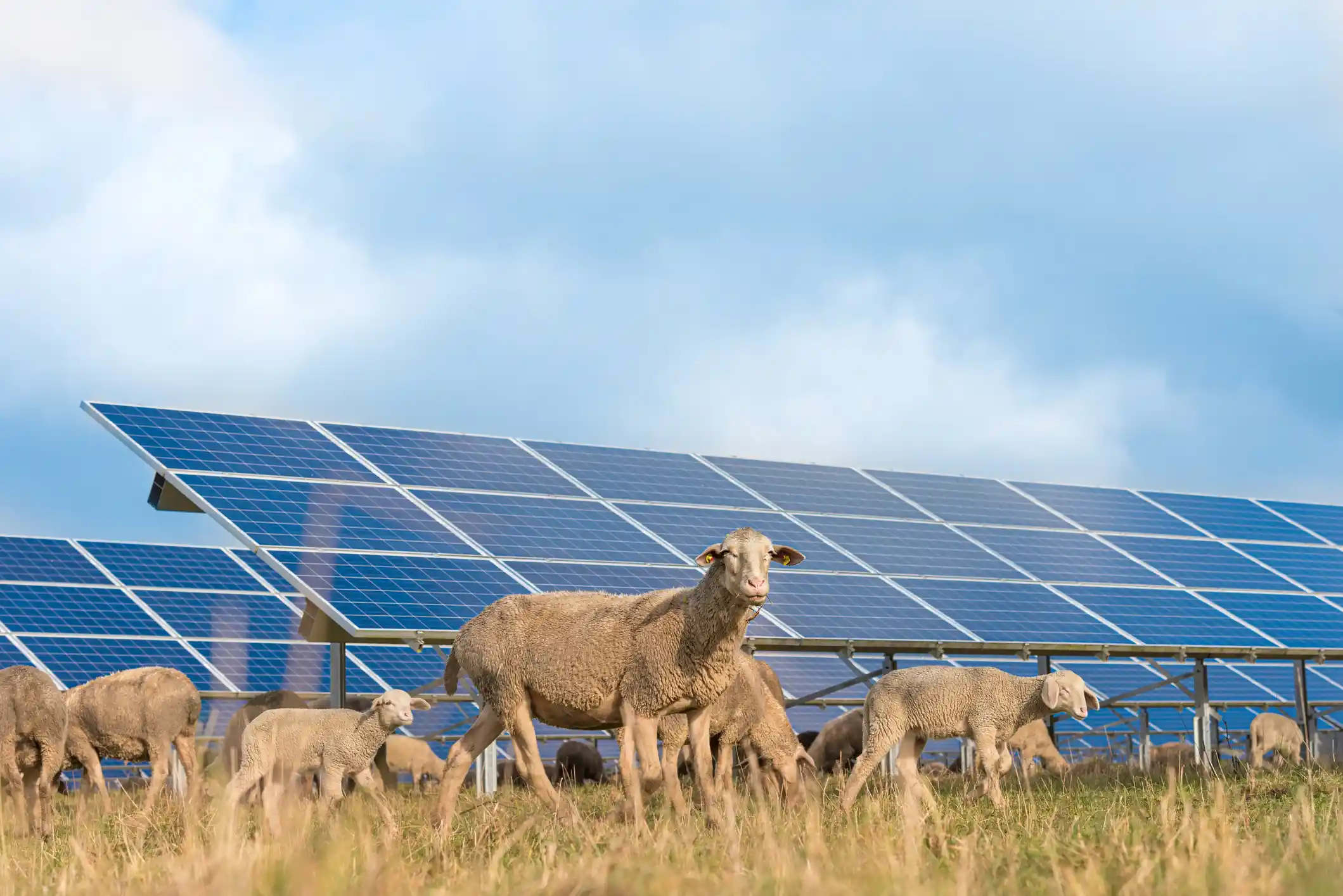

There have been many successful agrivoltaic projects around the world. Here are just a few notable ones.
Jack’s Solar Garden, Colorado
Jack’s Solar Garden is one of the most successful agrivoltaic projects in the United States. Located in Boulder, Colorado, this 1.2-megawatt (MW) array generates enough electricity to power over 300 homes while also supporting agricultural activities. Since 2021, Jack’s Solar Farm has produced more than 25,000 pounds of vegetables, herbs, and berries. It also includes a pollinator habitat and hosts various research and educational programs.
Daghio Solar Farm, Thailand
This project in northern Thailand combines utility-scale solar with vegetable and fruit farming. The shade provided by the solar panels helps reduce heat stress and water loss, leading to increased crop yields and improved soil health. This dual-use approach has supplied clean energy to the local community while enhancing the farm’s productivity.
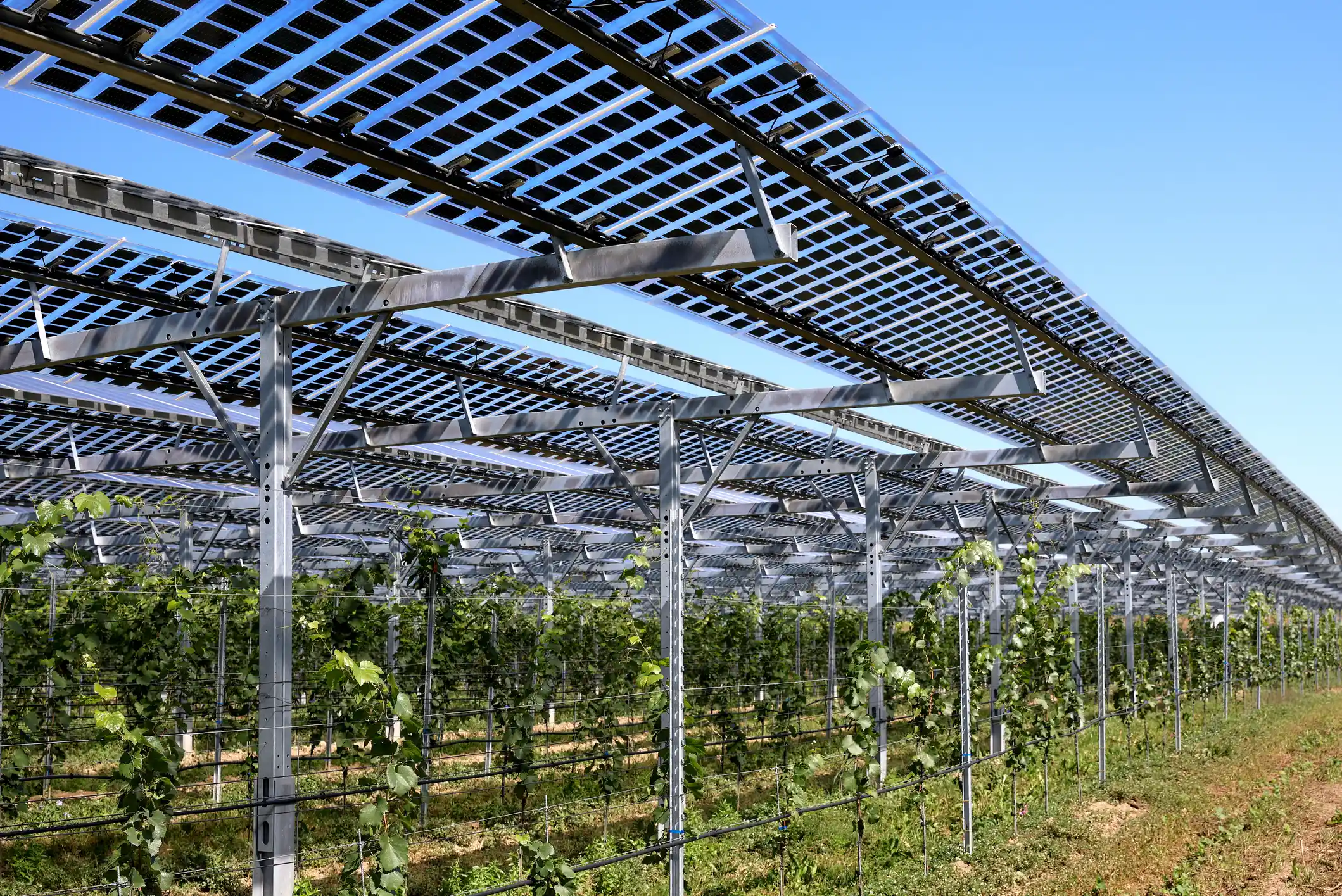
Projet Eole, France
Located in a vineyard in France, this project combines solar energy with grape production. The solar panels help protect the grapes from excessive sunlight and heat, improving their overall quality. This integration has provided clean energy to the local community while increasing the vineyard’s productivity and improving the quality of the grapes.
Overall, agrivoltaics helps amplify the positive environmental impact of solar power. It maximizes land use by making it more productive and helps promote biodiversity, lessening the environmental impact of utility-scale solar farms. Agrivoltiacs also have a positive impact on local economies by creating green jobs. As researchers improve technology, agrivoltaics will become an increasingly viable option for landowners who want to increase their land’s productivity and profitability.
At Shasta Power, we can help you take advantage of the benefits of utility-scale solar farms. We partner with you to develop and build solar energy projects directly on the land you already know and love. We can also help you create an agrivoltaic solar farm that increases your land’s potential. Shasta Power can help you maximize your property value while making a positive impact on the environment.
If you are interested in partnering with Shasta Power, visit our landowners page. You can also contact us to learn more about what we do and the benefits of partnership.